Read time 8 minutes
Microsoft Exchange Server has revolutionized professional email communication for businesses, making it more convenient and efficient both internally and externally, regardless of the company’s size. Microsoft has introduced several features in Exchange since it was first introduced in April 1996 to make the messages completely secure. But still, many threats are roaming around to damage the database. These threats hold the potential to make the Exchange database corrupt and inaccessible.
This Exchange database shows obstructions in mounting until you completely fix the corruption and repair corrupt EDB file. Let’s go through this article and learn about EDB corruption in detail and how we can resolve it from the server.
Why do you need to repair Exchange database?
Repairing Exchange database corruption is crucial to make the email communication and data accessible to all users. Here is why it’s essential to repair EDB file:
- Oversized database: When the size of the database increases beyond the allotted limit, it often causes issues for the users in executing their everyday operations. This becomes one of the primary reasons for corruption, leading the database to dismount itself.
- Abrupt system or server shutdown: Abrupt shutdown of system due to sudden power crashes introduces errors in committing transaction logs. Hence, it creates the need to fix the error so that the database inconsistency can be handled.
- Hardware failure: Anything from hard drive bad sectors or overheating of drives can cause damage in the Exchange database. Make sure to monitor the components of your installed hardware to avoid errors while working with it.
- Human errors: Human errors such as accidental deletion of mailboxes, improper or incorrect dismounting of database, or errors related to transaction logs entry can cause interruption in the database.
Types of Exchange database corruption
Majorly, there are two types of EDB corruption in an Exchange server. Before we discuss these methods of Exchange EDB repair in detail, it’s crucial to understand these two types. So, without a further ado, let’s start:
- Physical corruption: Physical corruption in the Exchange database is basically a result of failure or inefficiency in hardware you are using to operate your Exchange Server on. This is the lower form of EDB corruption, and you can easily repair the Exchange database just by repairing or replacing these components with new ones.
- Logical corruption: Logical corruption is something that occurs within multiple levels of the software. Jet engine database failure or invalid indexing are a few of the reasons that can lead to EDB file corruption.
Security features of Exchange Server 2019
The latest version of Exchange Server has upgraded the security features to safeguard the user mailboxes. Here are some prominent features:
- Windows Server Core Support: Using Exchange Server on Windows covers a lesser surface area. It reduces the chances of external attacks.
- Block external access to Exchange admin center (EAC) and the Exchange Management Shell: There is a Client Access Rule to block the external usage of the Exchange Admin Center and Exchange Management Shell.
- TLS 1.2 is the only version that’s enabled by default: For the betterment of client and server connections, the default encryption will be TLS 1.2 only. The older algorithms like DES, 3DES, RC2, RC4, and MD5 will remain disabled.
How to check corruption in Exchange mailbox?
In the Exchange Server 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019, run the following steps to check for corruption in your Exchange database and mailboxes.
- Open Eseutil.exe
- Run the eseutil /mh command to identify if the database is in Dirty Shutdown or Clean Shutdown state.
If the result shows you a Clean Shutdown state, your database is free from errors or corruption. However, if you find a Dirty shutdown state, there is corruption and inconsistency in your EDB files, and recovery is crucial.
Run the given PowerShell command using Exchange Management Shell to find if there’s corruption in the mailbox of Exchange 2013, 2016, and 2019.
New-MailboxRepairRequest
The command will help you find either out of the four corruption types: AggregateCounts, FolderView, ProvisionedFolder, and SearchFolder.
Eseutil helps in repairing the database only if the mailbox database is dismounted. However, the given PowerShell cmdlet helps repair corrupt Exchange database individual and multiple mailboxes without dismounting the online database.
How to repair corrupt Exchange database files?
Let’s discuss how to recover the lost data from a corrupt Exchange database and convert EDB file to PST.
Using Eseutil utility to repair EDB files
Eseutil is an inbuilt tool that serves various essential functions such as repairing corrupted Exchange databases, defragmenting them, verifying database integrity, and optimizing storage by reducing database size.
- Locate the Exchange Database
- To repair the database: eseutil /p
- To defragment the database: eseutil /d
- To restore the database: eseutil /r
- To verify checksum in the database: eseutil /k
- To check the database integrity: eseutil /g
- To do hard recovery: eseutil /c
- To display the headers, logs, or checkpoint files: eseutil /m
- To copy database and log files: eseutil /y
- First, dismount the database from Exchange.
Dismount-Database –Identity <name of the database>
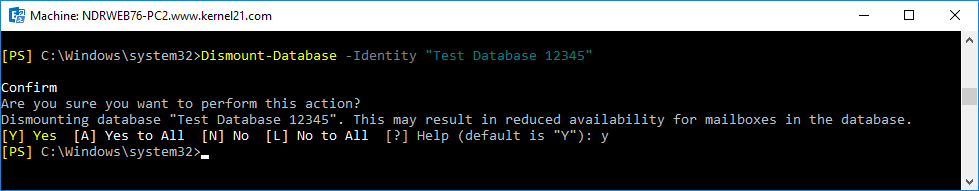
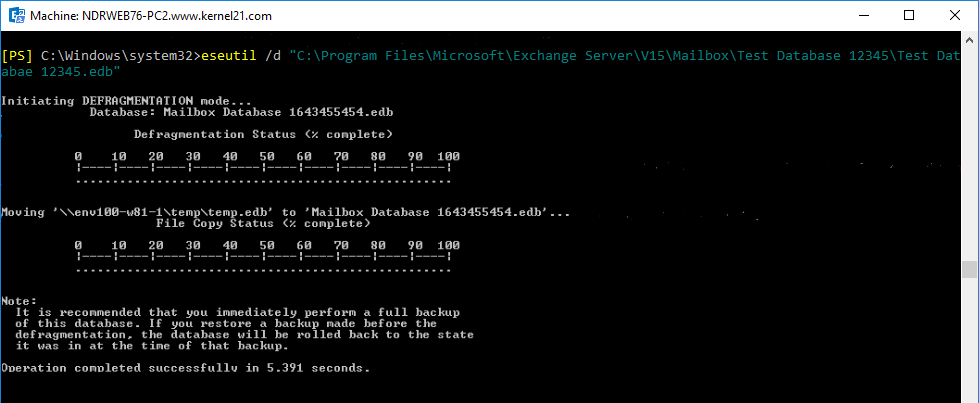
- Run Eseutil /d command
eseutil /d <name of the database> /T <location of temporary path>
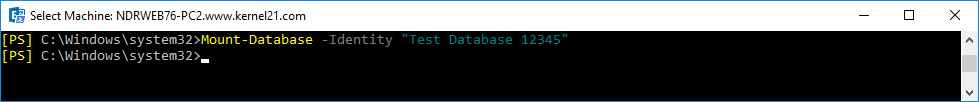
- After successfully running the Eseutil command, mount the database back to Exchange.
Mount-Database –Identity <name of the database>
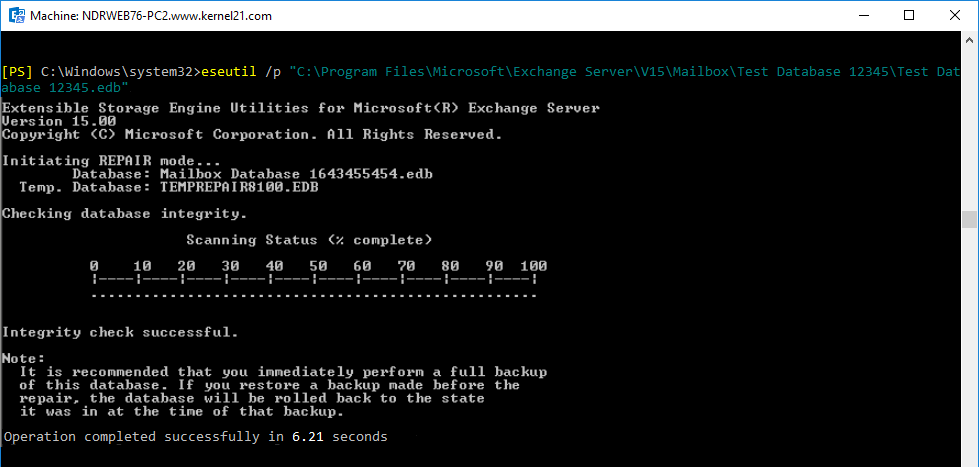
- Repair the database with Eseutil /p command.
eseutil /p <location of the database>
- Finally, run the new-mailbox repair request command to fix the errors in the database.
The default location of the tool in Exchange 2013/2016 is:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Bin
The Eseutil tool offers extensive functionality, allowing you to perform various actions using a range of switches:
New-MailboxRepairRequest -Database <name of the database> -CorruptionType <type of corruption>
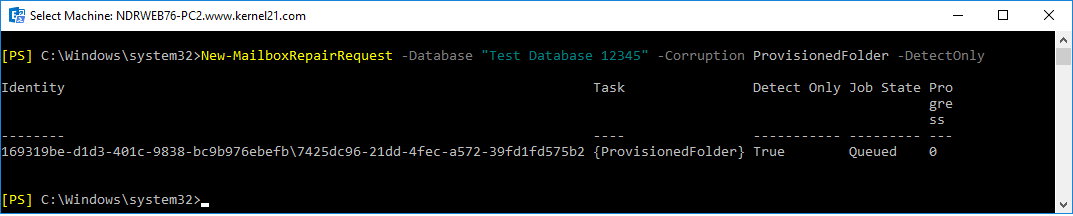
You can execute this command multiple times to eliminate all issues in the Exchange database.
Limitations of manual method of recovery
- It can take a lot of your time to recover all the mailboxes.
- You’ll need a huge storage to keep your mailboxes.
- One should have proper knowledge and hands-on experience in using the EseUtil.
- There is a high risk of data loss.
Users who are new to the Microsoft Exchange Server environment might not have technical knowledge and expertise to understand how to operate the utility. To avoid the complexity, users can proceed with the automated method of Exchange database repair, which doesn’t require you to dismount the database providing a hassle-free manner of doing it.
Conclusion
When there is a corruption in the Exchange database, administrators have two primary options for recovery: Microsoft’s Eseutil and Exchange server recovery software. While using ESEUTIL is helpful in performing soft and hard recovery, it may alter data integrity. In contrast, Kernel for EDB to PST Converter maintains data integrity and streamlines the Exchange EDB repair and recovery, making it a more efficient solution, particularly for complex or severely damaged databases. The software is also vital for restoring email flow, ensuring productivity, and preventing data loss in Exchange environments.







