An Exchange Server consists of Global Admin and Exchange admin roles. While Global admin has the highest privileges, Exchange admin role is more specific to tasks and compliance features.
An admin account in Exchange Server is responsible for all administrative activities. The administrator creates other accounts, mailboxes, and groups. All the activities related to accounts like security, backup, and restoration are also done by the administrator. In this article we’ll go through the process to create administrator account in Exchange 2013 and some pre-defined permissions that can be assigned to an Exchange administrator through the built-in role groups.
Responsibilities of an Exchange Administrator
With the Exchange administrator role, one can recover deleted mailbox items, set up archive and data retention policies, create a shared mailbox, and perform other crucial tasks. Apart from these routine jobs, occasional tasks like routine server maintenance are also done by the administrator.
- Constant support to the clients.
- Maintain the performance of the Exchange Server at the highest level.
- Upgrade the infrastructure of Exchange Server whenever required.
- Remove the mail-flow issues and improve it.
- Update the Exchange Server version.
- Perform the backup and restoration operations.
For better collaboration and communication, the administrator creates multiple groups and assign user-accounts to these groups. Another major responsibility of an Exchange Administrator is to troubleshoot whenever a disaster occurs. That's why the role of the Administrator is too important for the organization. Exchange administrator accounts have more rights and permissions than a regular user account.
How to Create an Exchange Admin Account?
Exchange administrator accounts have more rights and permissions than a regular user account. Here, we will go through a detailed narration to know about an Exchange administrator account and how do you can create one.
First, let us go through the step-by-step procedure of creating an admin account and assigning administrative roles:
Step 1. Login to Exchange Admin Center.
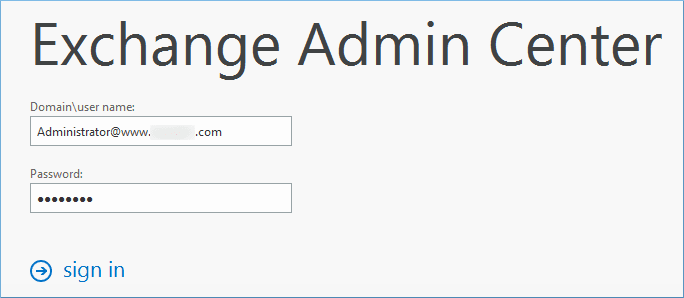
Step 2. In the permissions category, go to admin roles, and then select the category of Organization Management. Finally, click the Edit button.
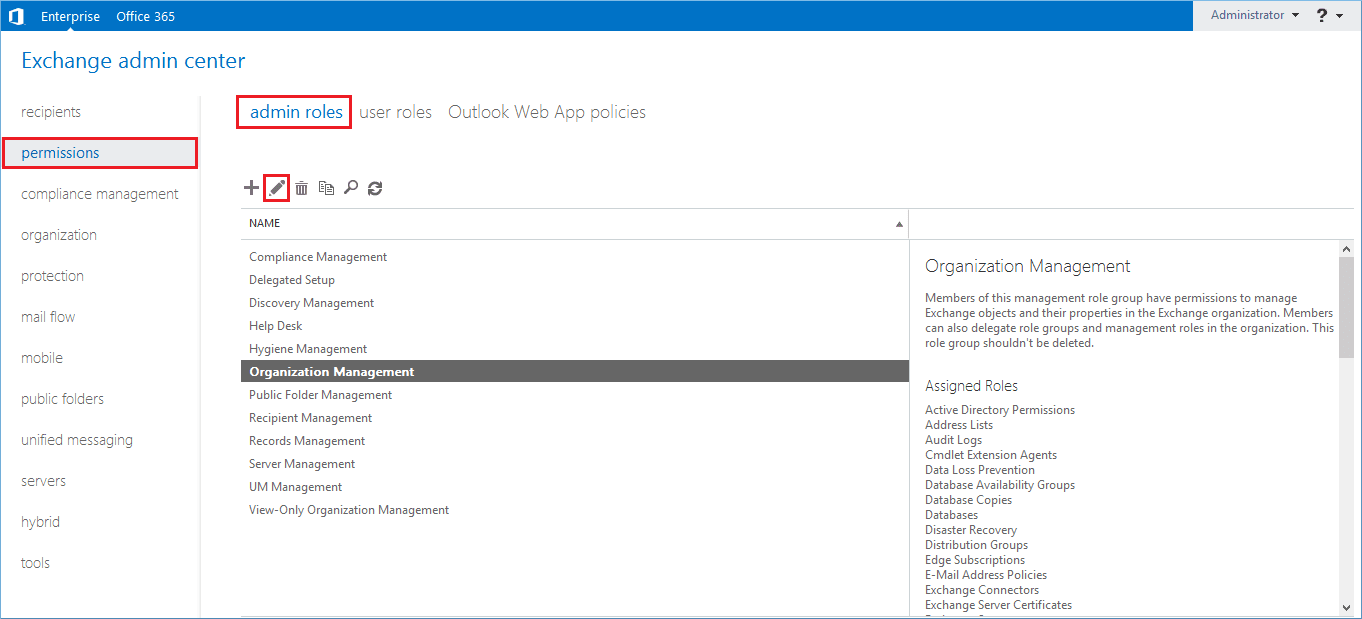
Step 3. Click the Add () button to add the member to the respective role group.
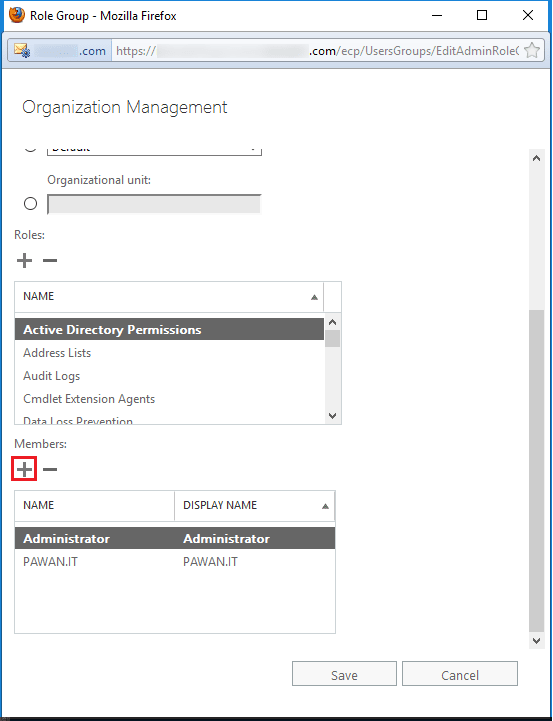
Step 4. Select the user which you need to add as an administrator. Click the Add button and then click OK.
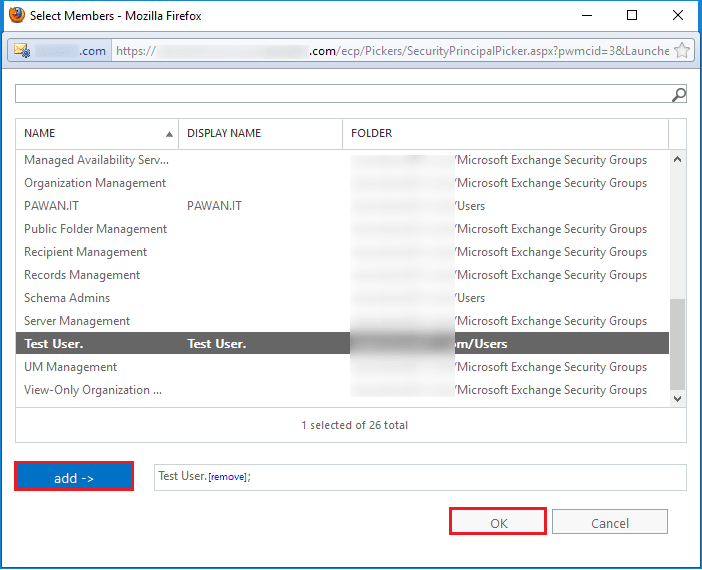
Step 5. The new user is now a member of the Organization Management. Click the Save button.
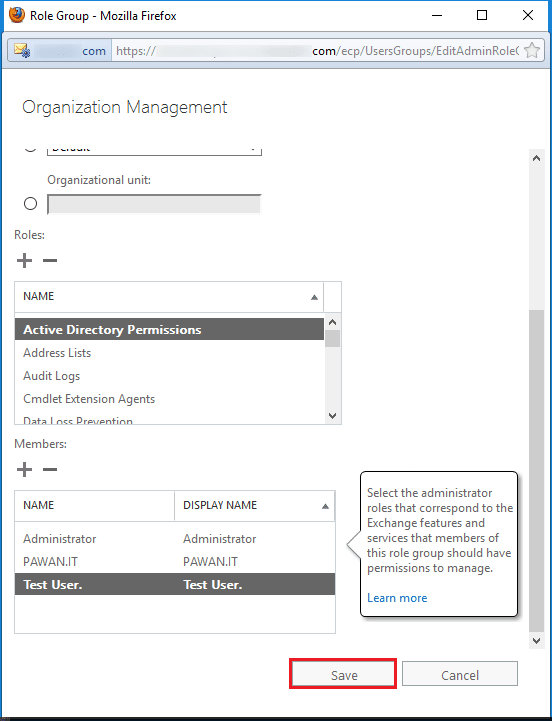
Step 6. You can see the new user in the list which has all the rights of the group.
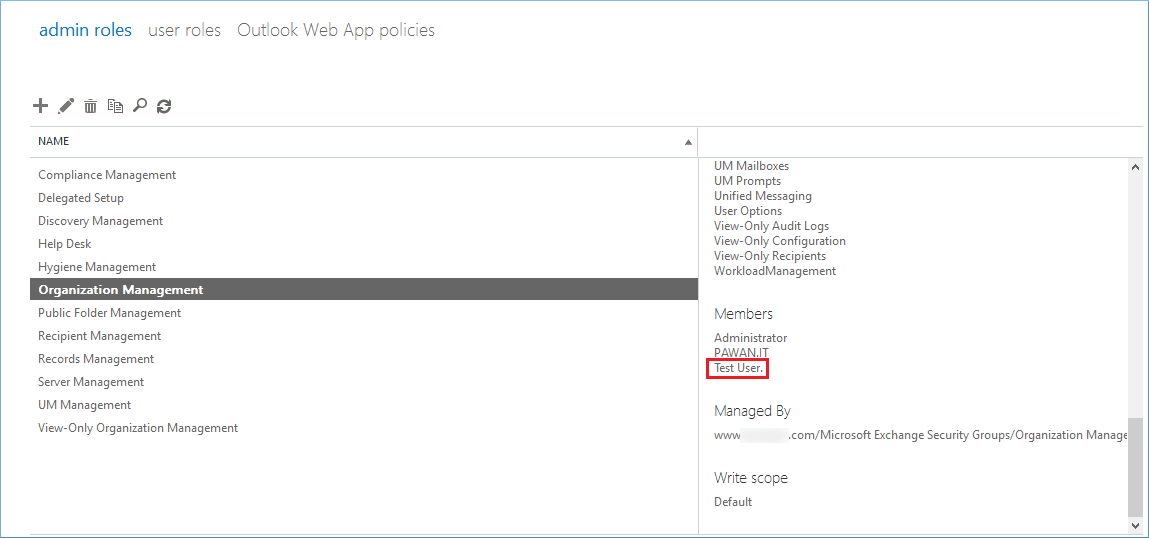
Once you create an Exchange administrator account, you should proceed and learn about the role-based groups. An administrator should have at least one role assigned to it. It can also have more than one role to perform multiple jobs in the Exchange Server environment.
For easy management of roles, Microsoft has created role groups which are special universal security groups. When the role is assigned to a group, then all the permissions associated with the role are automatically attached to the group members.
Essential Built-in Role Groups for an Exchange Administrator
Here is a brief list of various built-in role groups which the administrator can become a member.
Organization Management: The administrator members of the Organization Management will have administrative access to the Exchange Server and can perform almost all managerial tasks.
View-Only Organization Management: Administrator members of this group can view the properties of any object in Exchange Server.
Recipient Management: Administrator members of this group can create or modify Exchange Server recipients within the Exchange environment.
UM Management: Administrator members of this group can manage the Unified Messaging service configurations and settings.
Records Management: Administrator members of this group can modify the compliance features like retention policy tags, message classification, and mail flow rules.
Discovery Management: Administrator members of this group can search the data in the entire Exchange Server environment based on a specific criterion.
Public Folder Management: Administrator members of this group can manage and configure public folders in the whole Exchange Server.
Server Management: Administrator members of this group can modify server configurations for transport, unified messaging, client access, mailbox, and features like certificates, database copies, send connectors, virtual directories, etc.
Delegated Setup: Administrator members of this group can deploy the servers which were earlier provisioned by a member of the Organization Management Role group.
Compliance Management: Administrator members of this group can manage the compliance settings based on their organization policy.
Tips to Create an Exchange Admin Account
General users account in Exchange Server are vulnerable to cyberbreaches, phishing, and ransomware attacks. Due to this, there’s high risk in granting administrative privileges to general user accounts. When you create an admin account in Exchange Server, there’re certain tips that you can follow. These instructions will help you preserve the confidentiality of your business data.
- Create strong passwords that are a mix of alphabets (uppercase and lowercase), numeric, and special characters.
- Use multi-factor authentication to add an additional layer of security.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to allow administrative privileges.
- Change the passwords to admin quite frequently (at least every 90 days).
- Control and review the permissions regularly to avoid credential thefts.
- Use separate and dedicated workstations to perform administrative tasks in the server.
- Regularly update your software on all devices you access the admin account.
- Take recurrent backups of your database.
How to Secure Exchange Database from Data Loss?
As an Exchange administrator, it is your responsibility to secure the data while restricting the unauthorized accesses. Once you’re done creating an admin account in Exchange Server, you need to be proactive and regularly monitor all systems in the organization, otherwise you may end up losing data to cyber attackers.
One efficient practice you can include is regular backup of Exchange mailboxes. However, manual approaches can cause data loss or even disrupt the overall structure of the data. To avoid this situation, use a professional Exchange Server Recovery tool like Kernel for Exchange Server. It helps to retain the hierarchy of the mailbox database and save backup to PST files within your system.
Conclusion
With the help of Exchange admin center, you can create Exchange administrator account and use it to assign different roles. Nevertheless, it is important to assess the tasks that need administrative privileges before you allow the access. Since data security is a crucial aspect of every business, don’t forget to run regular Exchange Server backup for optimum data confidentiality. You can consider Kernel for Exchange Server that helps you save consistent backup of your mailboxes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Can I use this method to create an admin account in Exchange Server 2016?
A. The process to create Exchange admin account as mentioned above can be used for Exchange Server 2013 and all the advanced versions.
Q. How can you improve security in Exchange Server database?
A. In order to enhance the data security within your Exchange environment, you can implement RBAC to manage the user access. It allows the administrative privileges to any user account only when it is necessary. Role based access control on Exchange Server helps restrict access of unauthorized user into the database.
Q. What is the best and easiest way to backup Exchange database?
A. Though there are many native approaches available to take backup of your Exchange Server, a professional Exchange Server recovery tool would be the best bet. It helps to prevent data corruption and loss that may occur during the process.

