Read time 9 minutes
Microsoft has designed the Exchange Server as a robust application that creates a sizeable database with multiple GBs, each consisting of multiple mailboxes. Users are granted the authority to delete older or unwanted mailboxes to create space for new data. However, this authorization also increases the chance of unintentional or sudden mailbox deletions. To overcome such threats, Microsoft offers several tools that help administrators monitor unusual activity within Exchange. These tools include:
- Microsoft Exchange antispam and antimalware.
- Microsoft Exchange Online Protection.
- Exchange Analyzer.
- Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit.
- Microsoft Security Configuration Wizard.
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
- Microsoft Safety Scanner.
While these features reduce the risk of accidental data deletion from Exchange Server, there remains a possibility of users deleting mailboxes accidentally.
In Exchange Server 2016, you can Exchange recover deleted mailbox either manually or using third-party solutions. The process involves creating a user account and connecting it to the disconnected mailbox. However, this is possible only if the mailbox’s retention period has not expired.
Default mailbox retention period in Exchange 2016
In Exchange Server 2016, when you delete a mailbox, it does not get deleted permanently; instead, it is retained for a default period between 14-30 days. Within this retention period, users can Exchange restore deleted mailbox. However, after these 30 days, the mailbox will be removed permanently from the database.
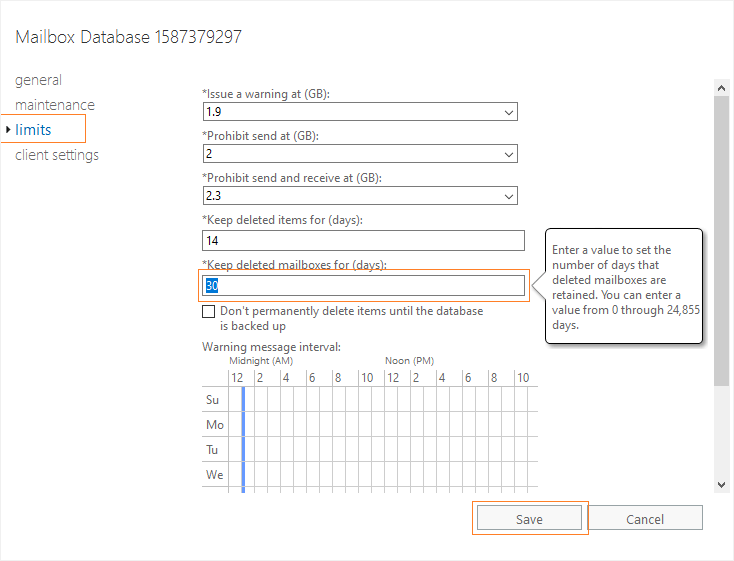
Configure mailbox retention period
To configure the mailbox retention period manually, you can use the Exchange Admin Center (EAC).
- In EAC, select servers on the left pane.
- Under the databases tab, select the required database and then click the edit icon.
- In the Limits option, modify the number of days in the Keep deleted mailboxes for (days) field (by default, the number is 30). You can adjust the default 30-day period to the number you would like to keep them for and then click Save. You can also mark the checkbox “Don’t permanently delete items until the database is backed up” to save your items from permanent deletion until you take back up of the database.
How to connect a deleted mailbox to a user account?
To restore a deleted mailbox, connect it to a user account. The process is similar for shared, linked, and resource mailboxes. This can be done using the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or Exchange Management Shell (EMS). Alternatively, you can use third-party tools to Exchange recover deleted mailbox, email, and other mail items.
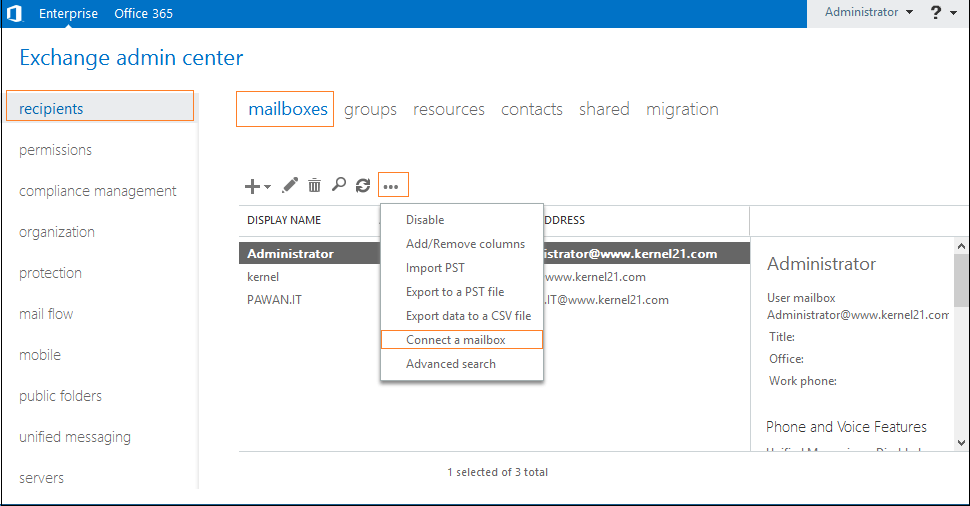
1st Solution: Connect a deleted mailbox to a user account using EAC
You can connect deleted mailboxes to user accounts using the Exchange Admin Center. The process is the same for all: linked, resource, and shared mailboxes.
- Open EAC and go to Recipients>Mailboxes.
- Click More(the three dots …) and then select Connect a Mailbox option.
- Choose a deleted mailbox from the list of disconnected mailboxes. Click Connect; click Yes.
- Now, you will receive a list of user accounts (not mail-enabled). Click the user account to which you want to connect the selected deleted mailbox.
- Retrieve the user from Active Directory (AD) Recycle bin to connect to a deleted user account again.
- If you can’t find the user or is deleted from the recycle bin, create a new AD user.
- Connect the disconnected user mailbox to this new user.
- Click the refresh icon to check the Status.
Note: When you delete an Exchange mailbox, mailbox and its related user in AD also get deleted and sent to the AD Recycle bin (if it’s enabled). If there’s no deleted AD user account, create a new one from the Exchange Admin Center and link the user to the disconnected mailbox. You can also do this through Exchange Management Shell usingConnect-Mailboxcmdlet.
Now, your Exchange will connect the deleted mailbox to the selected user account, so the deleted mailbox is available to the user again.
There are two ways to recover Exchange mailbox using Exchange Management Shell. Follow the section further to learn how to do it:
How to restore Exchange mailbox to a New User in Active Directory?
When you use Exchange Management Shell to connect a deleted mailbox to a user account, you need to specify the type of mailbox (shared, linked, room, or equipment mailbox).
Fetch all the available mailboxes from the Exchange Server using the following command:
Get-MailboxDatabase | Get-MailboxStatistics
The general syntax to Exchange restore deleted mailbox is:
Connect-Mailbox -Identity “mailbox name” -Database <database name=””> -User “AD user account name” -Alias <email=””></email></database>
You can use this method for deleted, shared, and linked mailboxes,but ensure that the AD user account you seek to link to the mailbox is disabled.
Run the command given below in the EMS to verify if you’ve restored the mailbox.
Get-User <identity>
How to restore a deleted mailbox in Exchange to an existing mailbox?
Run the New-MailboxRestoreRequest cmdlet in EMS to restore a deleted mailbox in Exchange. When you restore mailbox, the contents are copied to the existing mailbox, also known as target mailbox.
Once you restore mailbox, it will still be retained in the MB database until you delete it permanently. It will be permanently deleted after the retention period (30 days) expires, or you can remove it before that using the cmdlet Remove-StoreMailbox.
- Run Get-MailboxStatistics to get GUID values, including DisplayName, MailboxGuid, and LegacyDN of the deleted mailbox you want to restore
$dbs = Get-MailboxDatabase
$dbs | foreach {Get-MailboxStatistics -Database $_.DistinguishedName} | where {$_.DisconnectReason -eq “Disabled”} | Format-Table DisplayName,MailboxGuid,Database,DisconnectDate - Run the below cmdlet to select the target mailbox.
New-MailboxRestoreRequest -SourceStoreMailbox e4890ee7-79a2-4f94-9569-91e61eac372b -SourceDatabase MBXDB01 -TargetMailbox “Debra Garcia” -AllowLegacyDNMismatch
MBXDB01 is the source mailbox, and Debra Garcia is the name of the target mailbox here in the given example.
- Now run the Get-MailboxRestoreRequest cmdlet to check the Status.
- Don’t forget to verify the restore Exchange mailbox and check the contents of the target mailbox.
3rd Solution: Reconnect a deleted mailbox
Before starting, remember that not more than one user can connect to an Exchange mailbox (as GUIDs must be unique). To reconnect a deleted mailbox, we restored in previous steps:
- Start Exchange Server Manager and go to the mailbox store having disconnected mailboxes.
- Under the mailbox store, click Mailboxes.
- Then, click Clean up Agent from the right-click menu.
- Select the disconnected mailboxes for recovery and click Reconnect.
- Finally, select the related user account and then click OK.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that manual recovery is only possible within the retention period. You can restore deleted mailboxes in Exchange Server 2016 through EAC or EMS PowerShell commands. But, once the mailbox is deleted permanently, you can’t recover Exchange mailbox through a manual process. In that case, only professional Exchange Server recovery software like Kernel for Exchange Server can retrieve a permanently deleted mailbox from a database. The software repair corrupt Exchange database data along with deleted mailboxes and items. It will scan the database and present the Exchange restore deleted mailbox with complete data integrity.







