Read time 6 minutes
Exchange administrators often disconnect the mailboxes that are no longer needed. This can be because an employee is leaving the company, mailbox storage overflows or the Exchange Server is under migration or decommission. These Exchange disconnected mailboxes stay within the mailbox database for 30 days (by default). Once this timeframe is over, the server eliminates these mailboxes.
Exchange administrators must reconnect disconnected mailboxes to recover data within the retention period. The mailboxes can be restored or reconnected to an existing or new Active Directory user. PowerShell and Exchange admin center are the two native approaches to reconnect the disconnected mailbox. Let’s learn about them in detail.
What is an Exchange disconnected mailbox?
A disconnected mailbox in Exchange Server denotes a mailbox that has lost connection with its Active Directory user account. If the user has committed Disable-Mailbox or Remove-Mailbox cmdlets in Exchange Management Shell, then the mailbox shows such state. There can be two scenarios for a disconnected state:
- When the Exchange mailbox is disabled: The Exchange mailbox still exists in the mailbox database but in a disabled state, thus inaccessible. It remains in the disabled state until the retention period (default 30 days) is over. After that, it will be removed from the database.
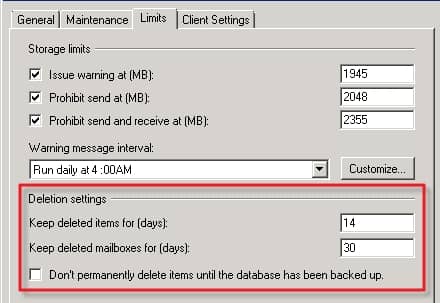
- When the Exchange mailbox is soft-deleted or deleted: Such mailboxes are also termed as disconnected mailboxes as a user cannot access it until they are connected back to the user account. A soft-deleted mailbox can be recovered within the retention period.
So, we have learned that a disconnected mailbox can be soft-deleted or disabled. A user can get to know if the mailbox still exists in the mailbox database by running this cmdlet in the Exchange Management Shell.
$dbs = Get-MailboxDatabase
$dbs | foreach {Get-MailboxStatistics -Database $_.DistinguishedName} |
where {$_.DisplayName -eq “<DisplayName>”} | Format-List DisplayName,Database,DisconnectReason
Note: Provide the mailbox display name in the place of the bold text in the above cmdlet.
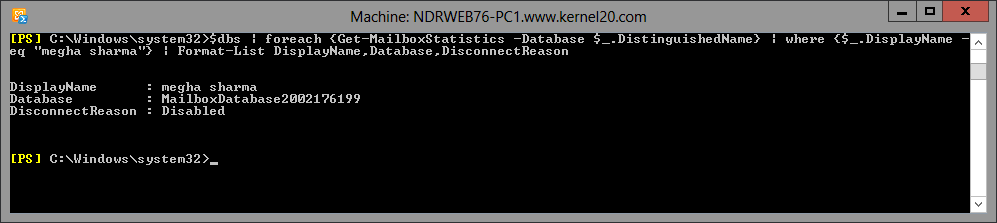
This output shows Display Name, Database and Disconnect Reason (either Disabled or Soft-deleted).
Now, to reconnect a disconnected mailbox in Exchange Server, Microsoft has provided two manual ways – using Exchange Admin Center or by executing cmdlets in the Exchange Management Shell. We are going to understand both the processes to reconnect Exchange Online disconnected mailbox one by one in detail.
Reconnect disconnected mailbox Exchange 2016 using EAC
It is the easiest process of the two and does not require any technical skills for execution. Perform the following steps sequentially for reconnecting a disconnected Exchange Serve mailbox.
Step 1. Login to Exchange Admin Center.
Step 2. Go to recipients > Mailboxes. Click … (More) and then click Connect a mailbox option from the drop-down list.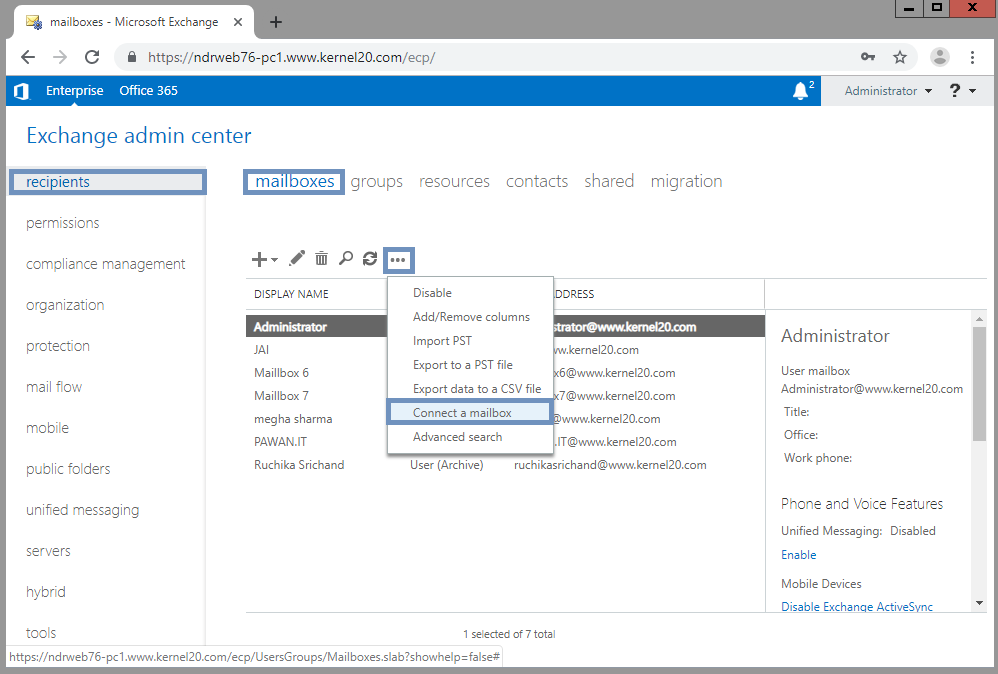
Step 3. Next, all the disconnected mailboxes will get listed. Select the mailbox and click the Connect icon.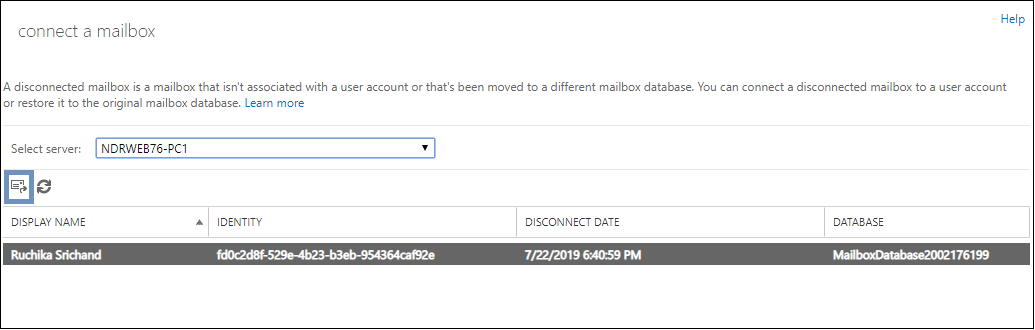
Step 4. The next dialogue box will give you the option to connect to the above user account or a different user account. Select the required option.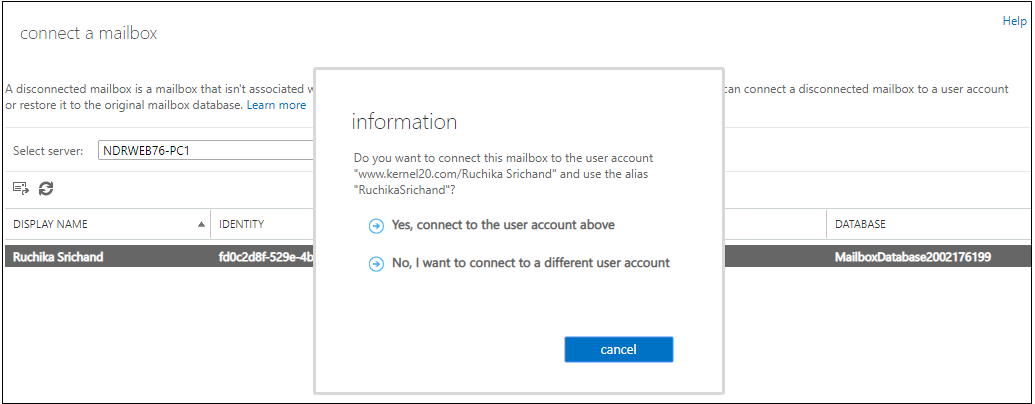
Note: If you select the second option, then a page will get opened with the option to select different mailbox types. User can select the desired option and proceed.
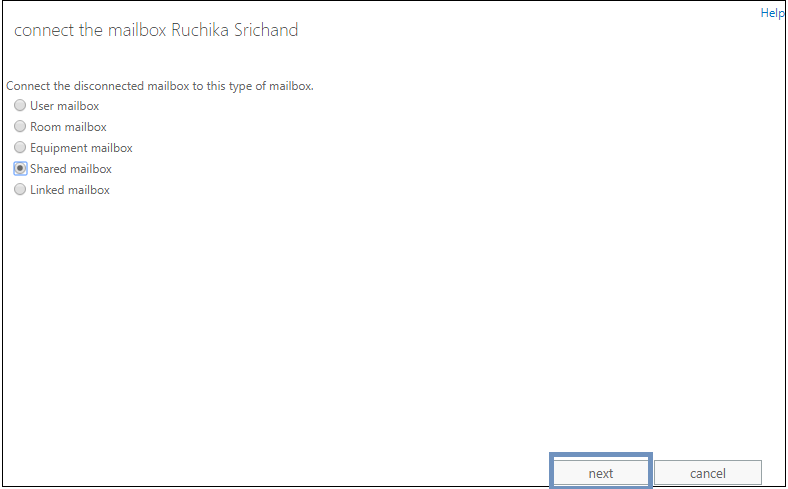
Step 5. Click Browse and add the desired mailbox of the selected type. Then click the Finish button.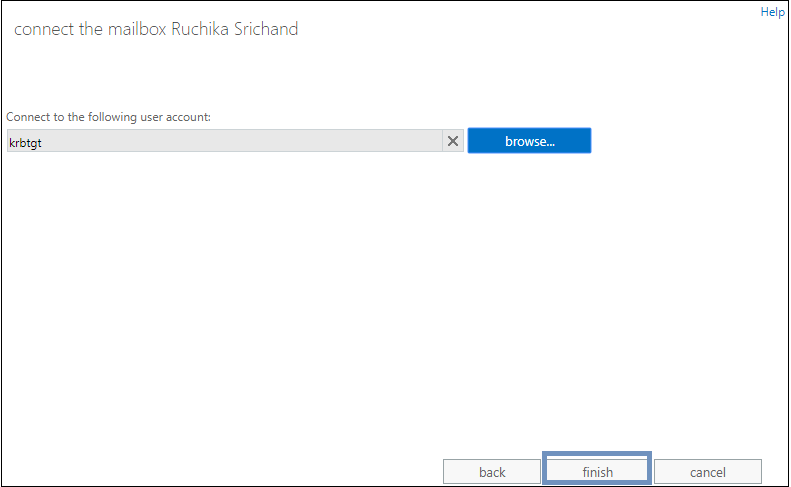
Step 6. The mailbox gets connected to the specified user account and will be out of the disconnected state.
Hence, reconnecting a disconnected mailbox is successfully performed through the Exchange Admin Center interface.
Reconnect a Disconnected Mailbox via Exchange Management Shell
This method is a little complex since you need to run the PowerShell cmdlets and for that you need to be technically sound.
Open the Exchange Management Shell. Wait till it connects to the Exchange Server. Now, run this command to reconnect the disconnected mailbox in Exchange Server:
Connect-Mailbox -Identity “<display name>” -Database <mailbox database name> -User “<display name>”
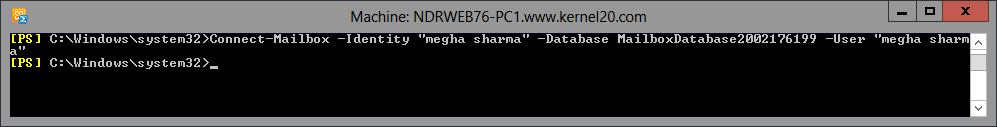
The mailbox will be available at its original location within connected to the user account. Also, users can connect this mailbox to other mailbox accounts, such as shared mailbox, linked mailbox, etc.
To connect the disconnected mailbox to the shared mailbox, run this command:
Connect-Mailbox -Identity “<shared mailbox display name>” -Database “<mailbox database name>” -User “<shared mailbox display name>” -Alias <name> -Shared
This explains that the mailboxes can be reconnected if disabled or soft-deleted (within the retention period), through the above-explained manual techniques. But these solutions will not work if the EDB file is corrupted. It means a disconnected mailbox cannot be reconnected if the Exchange database file is damaged or corrupted. It is quite a complex procedure if you run Eseutil for EDB Repair.
However, Kernel for Exchange Server, being a professional third-party software can help you recover corrupt EDB mailboxes including the deleted mailboxes flawlessly. It integrates powerful algorithms for fixing corruption. It provides many filters and saving options to recover Exchange mailboxes as per your needs.
Wrapping up
With the help of the manual methods explained in the article, you can reconnect disconnected mailbox Exchange 2016 again. But, if there’s corruption in the database, these methods will not give the fruitful results. So, you should repair the database using Kernel for Exchange Server Recovery software and recover the mailbox. The software provides a robust solution for the recovery of mailboxes after EDB file corruption.







