Read time 4 minutes
Whenever you switch on your PC or laptop devices, the startup function triggers a search for the boot program sequence in the local drives. If the boot sequence is located, the system will start without any uncertainties or errors. But if it fails to locate the boot sequence, then the startup fails.
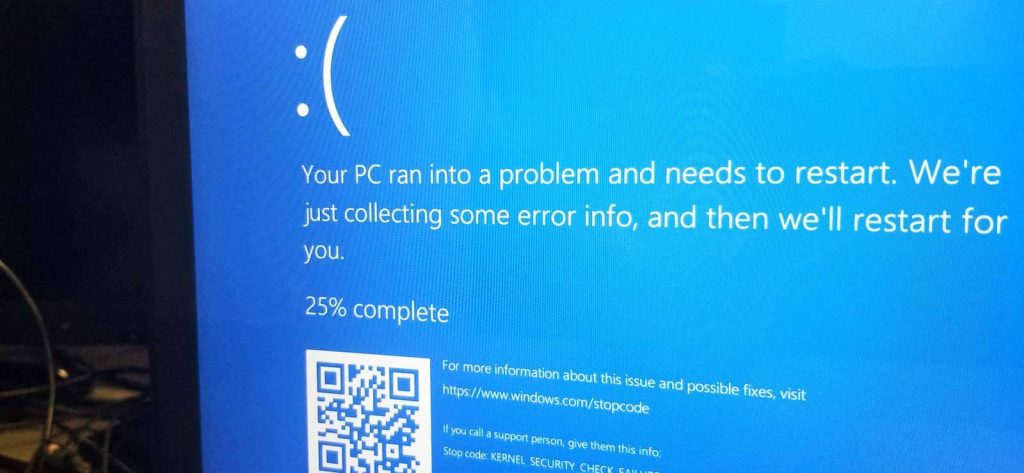
Now, if you are facing a similar scenario, i.e., while initiating the startup, your system fails to locate the boot sequence and prompts an error message – “Your PC ran into a problem and needs a restart,” the chances are that either the startup files have gone corrupt or there is some physical damage to your hard drives. The main question here is, what will you do, and what are the steps you will take to fix the issue?
Well, before getting into the cause and methods to undo the clutches of this fatal error. Let us first understand a bit more about the unbootable state of systems.
Unbootable Systems
Typically, when your PC’s or laptop devices are switched on, the computer system prepares itself to execute the start instruction. This process involves locating the boot-up sequence in the BIOS (Basic Input Output System). BIOS of a system is the first program that runs when you switch on your computing devices, whereas, the boot-up sequence is a set of instructions intended to execute the operating system that resides within the BIOS.
If the PC is unable to locate the boot-up sequence within the BIOS, the startup instruction is denied, and you’ll receive error messages on your screen.
A system, when it is in an unbootable state is hard to repair, and the data inside them ultimately gets inaccessible. There are, however, methods available to repair unbootable PCs or laptops, but it requires the physical removal of the local hard drive configured inside the CPU. Therefore, to recover data from Windows first, we need to migrate the affected hard drive to some other system.
Factors that lead to the Unbootable State of Computer Systems
Let us throw some light on the reasons that lead to the unbootable state of your computing devices. Some common causes are listed below:
- System files required to invoke the boot-up sequence have gone corrupt.
- Bad sectors on hard drives resisting the startup process.
- Virus Intrusions sometimes corrupt the system files.
- Operating system corruption can also be a root cause of an unbootable system state.
- Sometimes BIOS corruption also leads to the unbootable state of the PCs and laptops.
Method to recover data from unbootable devices
As we have discussed earlier, the foremost method to fix unbootable hard drives involves the removal of the affected hard drive and then using it as an external storage device on some other computer. However, one needs to be very precise while pulling out your hard drive.
Follow the steps given below in order to retrieve the data from unbootable hard drive, manually:
- Unplug your PC or laptop from the power source. In simple terms, switch off the power supply. Remove the battery, in case you are using a laptop.
- Disassemble your PC or laptop, locate the hard drive by and unplug all the hard drive cables.
- Unscrew the hard drive and put it out of the case.
- If required, insert the hard drive into an external hard drive case.
- Connect the hard drive to a new PC or laptop.
- Reboot the new system from its standard Operating System on the main drive.
- Now, you can access the data residing in that unbootable hard drive, copy the data, and unplug the hard drive.
In case, you are unable to access the data even after installing the hard drive to some other PC or laptop. Then, either the hard drive has gone corrupt, or the data has been deleted somehow. For such scenarios, you must try a third-party Windows data recovery tool.
Kernel for Windows Data Recovery is a prominent tool to recover lost or permanently deleted data from hard drives. You can easily recover inaccessible data through this software. Also, you can preview the recovered data before saving them to your local hard drives. Moreover, the tool works exceptionally well on almost all Windows versions.